You could load resources using ClassLoader.getResourceAsStream() or Class.getResourceAsStream(). Important thing to note is that Class.getResourceAsStream (String) delegates the call to ClassLoader.getResourceAsStream(String). You can see the same below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) { name = resolveName(name); ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0(); if (cl==null) { // A system class. return ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(name); } return cl.getResourceAsStream(name); } |
resolveName(name) will add a package name prefix if the name is not absolute. Remove leading “/” if name is absolute. What does this mean? This means that if we pass just “test.properties” to getResourceAsStream it will resolve it to “com/my/test.properties” (assuming your current package is com.my). If we pass “/test.properties” it will assume you’re passing an absolute path and remove “/” making it just “test.properties”. Remember your classpath must have “com/my/test.properties” or “test.properties” depending on what you pass to getResourceAsStream(). Now, if you are using ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream() directly we know from the above code that it expects absolute paths without the “/” in the beginning.
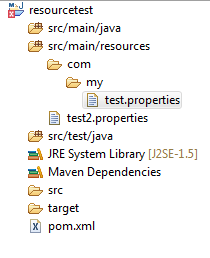
Here is a sample folder structure and App.java the reads properties files from the classpath. Remember that the src/main/resources folder must be added (and usually is added) to the classpath.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | package com.my; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Properties; public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { String var = null; Properties properties = new Properties(); try { InputStream in = App.class.getResourceAsStream("test.properties"); properties.load(in); var = properties.getProperty("my.prop"); System.out.println(var); in = App.class.getResourceAsStream("/test2.properties"); properties.load(in); var = properties.getProperty("my.prop"); System.out.println(var); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |